Histological and Biochemical Changes Associated with Targeting of Adrenergic B3 receptor
Abstract
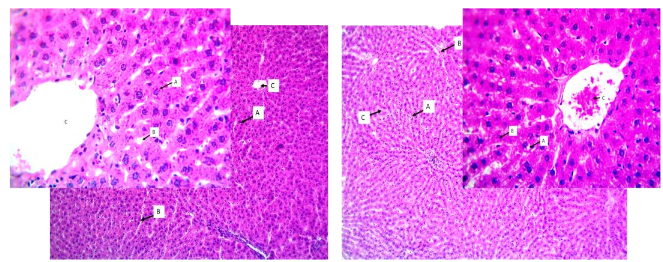
Overactive bladder (OAB) is regarded as a combination of symptoms associated with the urgency of urination, urinary frequency, with or without incontinence and nocturia which tends to increase with age in both males and females. Through this study, we aim to analyze the changes in liver enzymes and hepatic tissue histology after the use of mirabegron for three months. A double-blinded randomised control trial was held on the sample size of 10 rats which were divided into two groups, a controlled group and a mirabegron induced for three months. NaCl was used as a placebo. Biochemical analysis of liver enzyme was done through a blood sample taken from the femoral nerve followed by a histopathological examination. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) level of the controlled group was 105 U/L which was reduced to approximately 87 U/L on the other hand, in the case of mirabegron induced group the levels reduced from 122.5U/L to 90 U/L, glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GPT) remained constant on controlled group 27U/L meanwhile in case of mirabegron group the level fell from 34U/L to 19U/L. the serum level of alkaline phosphates remained the same in the controlled group i.e. 300U/L but a reduction has been found in the mirabegron group from approximately 375U/L to 310U/L. These results indicate mirabegron as the best choice of drug for OAB with the hepatoprotective mechanism of action with better efficacy and tolerability.