Characterizing the Virulence of Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from Wounds: An Experimental Approach
Abstract
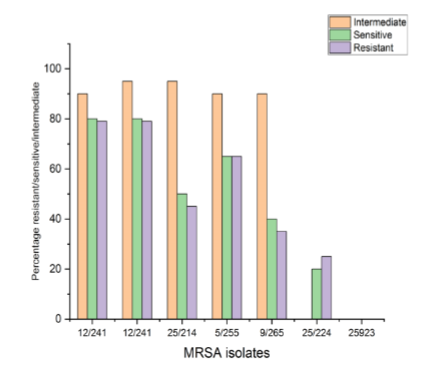
In consequence of the feared superbug Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), people are gravely at risk for major health issues. The severity of an infection is influenced by the existence of virulence factors and medication resistance. The two most drug-resistant and virulent MRSA isolates that best exhibit the early characteristics of intestinal adhesion were chosen for this investigation in an effort to designate them for potential future using postbiotics and probiotics as antagonists to treat MRSA infections. The bacterial agent's level of pathogenicity towards the organism—i.e., its capacity to wreak disease is referred to as virulence. The virulence factors offer the virus certain qualities that allow it to fight the host's natural defences and so produce illness. The development of diverse enzymes, antibiotic resistance, and bacterial toxins are the most crucial of these elements since they all aid the pathogen's ability to adapt to varied situations. The results of the virulence factor assays revealed that each of the 50 MRSA isolates developed biofilm and hemolysin enzyme type beta and coloured blue in Gramme stain.
References
Baddour, L. M. (1994). Virulence factors among gram-positive bacteria in experimental endocarditis. Infection and immunity, 62(6), 2143-2148.
Hussain, M., Becker, K., von Eiff, C., Schrenzel, J., Peters, G., & Herrmann, M. (2001). Identification and characterization of a novel 38.5-kilodalton cell surface protein of Staphylococcus aureus with extended-spectrum binding activity for extracellular matrix and plasma proteins. Journal of bacteriology, 183(23), 6778-6786.
Schwarz, C., Töre, Y., Hoesker, V., Ameling, S., Grün, K., Völker, U., ... & Hoerr, V. (2021). Host-pathogen interactions of clinical S. aureus isolates to induce infective endocarditis. Virulence, 12(1), 2073-2087. DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1960107.
Kadkhoda, H., Ghalavand, Z., Nikmanesh, B., Kodori, M., Houri, H., Maleki, D. T., ... & Eslami, G. (2020). Characterization of biofilm formation and virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from paediatric patients in Tehran, Iran. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 23(5), 691. DOI: 10.22038%2Fijbms.2020.36299.8644
Silva, V., Hermenegildo, S., Ferreira, C., Manaia, C. M., Capita, R., Alonso-Calleja, C., ... & Poeta, P. (2020). Genetic characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from human bloodstream infections: Detection of MLSB resistance. Antibiotics, 9(7), 375. DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics9070375
Cheung, G. Y., Bae, J. S., & Otto, M. (2021). Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence, 12(1), 547-569.
Pätzold, L., Brausch, A. C., Bielefeld, E. L., Zimmer, L., Somerville, G. A., Bischoff, M., & Gaupp, R. (2021). Impact of the histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein HPr on carbon metabolism and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms, 9(3), 466.
Parai, D., Banerjee, M., Dey, P., & Mukherjee, S. K. (2020). Reserpine attenuates biofilm formation and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbial Pathogenesis, 138, 103790.
Liu, L., Shen, X., Yu, J., Cao, X., Zhan, Q., Guo, Y., & Yu, F. (2020). Subinhibitory concentrations of fusidic acid may reduce the virulence of S. aureus by down-regulating sara and saers to reduce biofilm formation and α-toxin expression. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 25.
Nataraj, B. H., Ramesh, C., & Mallappa, R. H. (2021). Characterization of biosurfactants derived from probiotic lactic acid bacteria against methicillin-resistant and sensitive Staphylococcus aureus isolates. LWT, 151, 112195. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112195
Liu, L., Shen, X., Yu, J., Cao, X., Zhan, Q., Guo, Y., & Yu, F. (2020). Subinhibitory concentrations of fusidic acid may reduce the virulence of S. aureus by down-regulating sara and saers to reduce biofilm formation and α-toxin expression. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 25.
Dehbashi, S., Tahmasebi, H., Zeyni, B., & Arabestani, M. R. (2021). Regulation of virulence and β-lactamase gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus isolates: cooperation of two-component systems in bloodstream superbugs. BMC microbiology, 21(1), 192.
Gungor, C., Barel, M., Dishan, A., Disli, H. B., Koskeroglu, K., & Onmaz, N. E. (2021). From cattle to pastirma: Contamination source of methicillin susceptible and resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) along the pastirma production chain. LWT, 151, 112130. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112130
Muñoz-Silvestre, A., Penadés, M., Selva, L., Pérez-Fuentes, S., Moreno-Grua, E., García-Quirós, A., ... & Viana, D. (2020). Pathogenesis of intradermal staphylococcal infections: Rabbit experimental approach to natural Staphylococcus aureus skin infections. The American Journal of Pathology, 190(6), 1188-1210. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.01.019
Hassan, M. A., Abd El-Aziz, S., Elbadry, H. M., Samy, A., & Tamer, T. M. (2022). Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance profile, and characterization of multi-drug resistant bacteria from various infected wounds in North Egypt. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 29(4), 2978-2988. DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.01.015
Wang, W., Bao, X., Bové, M., Rigole, P., Meng, X., Su, J., & Coenye, T. (2022). Antibiofilm activities of borneol-citral-loaded Pickering emulsions against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in physiologically relevant chronic infection models. Microbiology Spectrum, 10(5), e01696-22.
Senobar Tahaei, S. A., Stájer, A., Barrak, I., Ostorházi, E., Szabó, D., & Gajdács, M. (2021). Correlation between biofilm-formation and the antibiotic resistant phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus isolates: a laboratory-based study in Hungary and a review of the literature. Infection and drug resistance, 1155-1168.
Abbas, H. A., Shaker, G. H., Mosallam, F. M., & Gomaa, S. E. (2022). Novel silver metformin nano-structure to impede virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. AMB Express, 12(1), 1-13.
Jain, S., Chowdhury, R., Datta, M., Chowdhury, G., & Mukhopadhyay, A. K. (2019). Characterization of the clonal profile of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from patients with early post-operative orthopedic implant based infections. Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials, 18(1), 1-7.
Budzyńska, A., Skowron, K., Kaczmarek, A., Wietlicka-Piszcz, M., & Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. (2021). Virulence factor genes and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from blood and chronic wounds. Toxins, 13(7), 491.
Amissah, N. A., Chlebowicz, M. A., Ablordey, A., Tetteh, C. S., Prah, I., Friedrich, A. W., ... & Rossen, J. W. (2017). Virulence potential of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Buruli ulcer patients. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 307(4-5), 223-232.
Aung, M. S., Urushibara, N., Kawaguchiya, M., Aung, T. S., Mya, S., San, T., ... & Kobayashi, N. (2011). Virulence factors and genetic characteristics of methicillin-resistant and-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Myanmar. Microbial Drug Resistance, 17(4), 525-535.
Shettigar, K., & Murali, T. S. (2020). Virulence factors and clonal diversity of Staphylococcus aureus in colonization and wound infection with emphasis on diabetic foot infection. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 39, 2235-2246.
Rasmi, A. H., Ahmed, E. F., Darwish, A. M. A., & Gad, G. F. M. (2022). Virulence genes distributed among Staphylococcus aureus causing wound infections and their correlation to antibiotic resistance. BMC Infectious Diseases, 22(1), 652.
Tkaczyk, C., Jones-Nelson, O., Shi, Y. Y., Tabor, D. E., Cheng, L., Zhang, T., & Sellman, B. R. (2022). Neutralizing Staphylococcus aureus Virulence with AZD6389, a Three mAb Combination, Accelerates Closure of a Diabetic Polymicrobial Wound. Msphere, 7(3), e00130-22. DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00130-22
Yousif, S. M., Abakar, A. D., Nour, B. Y., Ibrahim, S. O., Elhasan, O. M. A., Yousif, M. A., ... & Ahmed, E. A. (2021). Frequency and antimicrobials susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus associated with wound infections in surgery department, wad madani teaching hospital, sudan. Pharmacology & Pharmacy, 12(12), 334-343.
Qu, S., Liu, Y., Hu, Q., Han, Y., Hao, Z., Shen, J., & Zhu, K. (2020). Programmable antibiotic delivery to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus through precision therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 321, 710-717.
Duwadi, K., Khadka, S., Adhikari, S., Sapkota, S., & Shrestha, P. (2020). Bacterial etiology of wound exudates in tertiary care cancer patients and antibiogram of the isolates. Infectious Diseases: Research and Treatment, 13, 1178633720952077.
França, A., Gaio, V., Lopes, N., & Melo, L. D. (2021). Virulence factors in coagulase-negative staphylococci. Pathogens, 10(2), 170.
Vlaeminck, J., Raafat, D., Surmann, K., Timbermont, L., Normann, N., Sellman, B., ... & Malhotra-Kumar, S. (2020). Exploring virulence factors and alternative therapies against Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Toxins, 12(11), 721.